
- Git create branch command update#
- Git create branch command code#
- Git create branch command download#
Git create branch command code#
Let’s make a change to our code - first we’ll… whooaooaaaaa there! We’re going to use terminology here which we’ll need to explain and point at a state diagram to understand fully. As we’ve only just created this new branch of course, there are no updates.
Git create branch command update#
This will switch our branch and update our working directory should the code bases be different. We want to jump into the feature/unzip branch to begin coding our new feature, so to switch branches we’ll use the checkout command: Incidentally, you can view all branches, including remote branches by adding a couple of flags: git branch -av. First of all, we see our new branch has been created, and secondly, our active branch we’re working on is master, rather than the new branch. Although there was no feedback from this command, we can view all our branches by using the same command, but without a parameter: In this case we’ve been very sensible with our naming so it’s clear to read from the branch name that we’re creating the unzip feature for our ZipRebel project. So how do we create our branches? Well that bit is easy! Simply use the branch command passing in the name you’d like to call it, as follows: This is an important best practice in my opinion as keeping your new feature code separate from other changes in your master allows you to easily switch back and forth between branches without cross-polluting your code. If we were to create a new feature for example, we should consider creating a new branch for all of our feature code. Remote: Total 94 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 94 Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/sjmaple/myProject/.git/ Once this is done, we’re able to start our workflow! Here are the two examples in action on the ZipRebel project: The difference being of course that you would use the init command to create a repository from scratch, whereas you’d use clone to literally clone, or copy an existing repository into the directory you ran the command from. Both of which give you a repository in which you can manage your source code. Well, we’ll start at the beginning of course! In the beginning, Git created init and clone.
Git create branch command download#
At the end of the article, you can download a one-page Git command line cheat sheet rich with the Git commands of champions, the gems that make your SCM a pleasure to work with, the… ok, enough’s enough, let’s get down to business. Today we'll walk through some Git basics, including Git commands like pull, push, and fetch. With every great tool, there is a CLI which compliments all the great features and options, which leads to a vast number of things you need to remember and be expected to recall within a keystrokes notice. If you also provide a SHA-1 hash of a specific revision, your new branch will use that commit as its starting point.In this post, we’re looking at one of the most successful source code management tools available today, Git.
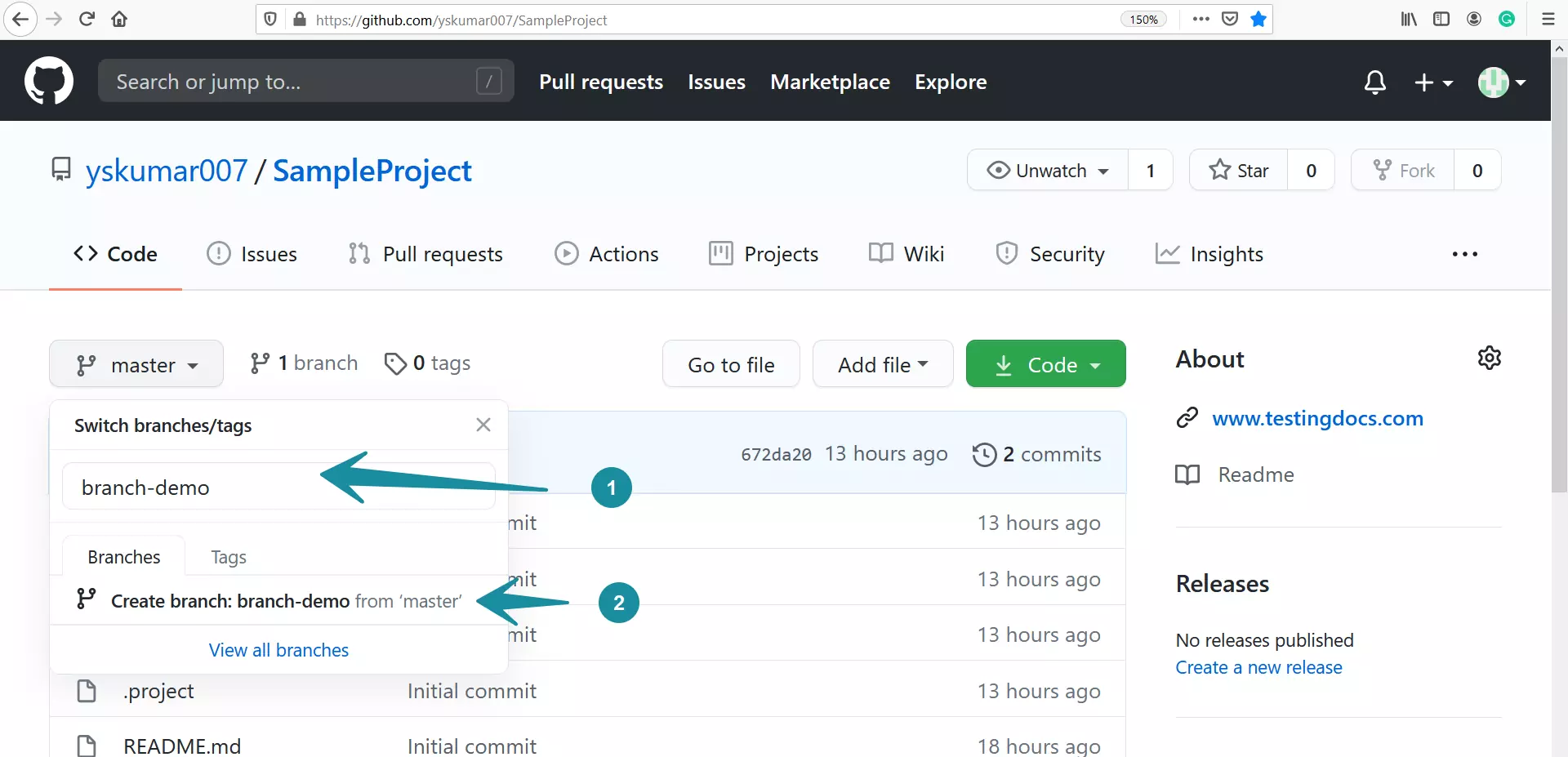
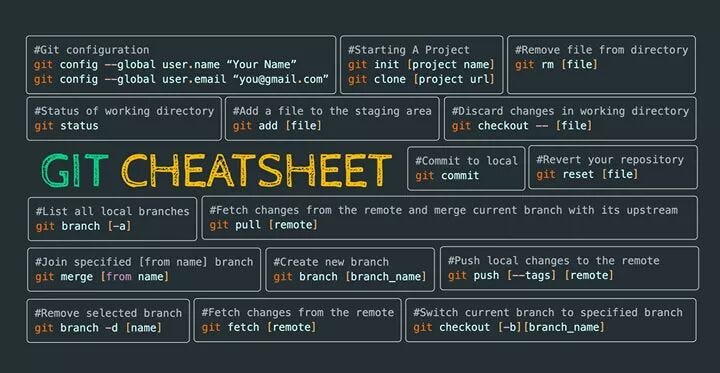
Provides more information about all your branches. It's the go-to command when it comes to managing any aspect of your branches - no matter if in your local repository or on your remotes. The "branch" command helps you create, delete, and list branches.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
